Species Synonym(s): None
Common Name(s): Virginia pepperweed, broadleaved pepperweed, tall whitetop, broadleaved peppergrass
Family: Brassicaceae (Mustard Family)
Family Synonym(s): None
Native Range (GRIN):
Selected images from Bugwood.org
Landscape Ornamental Use (GRIN): No
All Uses (GRIN): Flavoring, Vegetable, Potential seed contaminant
Summary: perennial pepperweed (Lepidium latifolium) is a Wetland/Terrestrial species.
Mid-Atlantic Coastal Plain regions
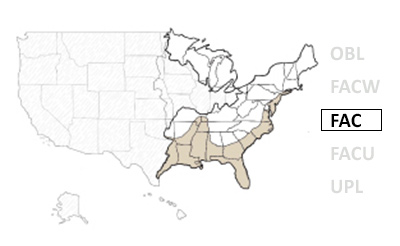
Mid-Atlantic Piedmont and Mountain regions
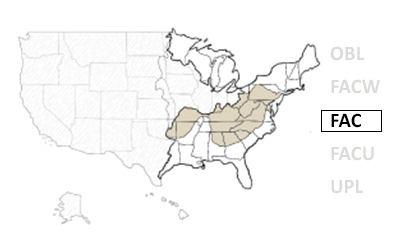
Northern parts of PA and NJ (and beyond)


OBL (Obligate wetland): Almost always occurs in wetlands (estimated probability > 99%) under natural conditions

FACW (Facultative wetland): Usually occurs in wetlands (estimated probability 67% - 99%), but occasionally found in non-wetlands

FAC (Facultative): Equally likely to occur in wetlands (estimated probability 34% - 66%) or non-wetlands

FACU (Facultative upland): Usually occur in non-wetlands (estimated probability 67% - 99%), but occasionally found in wetlands (estimated probability 1% - 33%)

UPL (Obligate upland): Occur almost always (estimated probability > 99%) in non-wetlands under natural conditions
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: Dilleniidae |
| Order: Capparales |
| Family: Brassicaceae |
| Genus: Lepidium |
| Subject: Lepidium latifolium L. |