Brazilian peppertree
(Schinus terebinthifolia)
Overview
Brazilian peppertree is a broadleaved, evergreen shrub or small tree that invades natural and disturbed areas in Hawaii, Florida, Texas and California. Plants can grow to 30 ft. (9 m) tall. The alternate, dark green leaves are pinnately compound and slightly toothed along leaflet margins. Leaflets are opposite along a (usually) winged rachis and 1-2 in. (2.5-5.1 cm) long. Leaves smell strongly of pepper or turpentine when crushed. Trees are dioecious with clusters of small, white, 5-petaled flowers developing in the leaf axils of young stems. Trees flower year-round, but flowers are most concentrated in the fall. Fruit are small, bright red berries. Brazilian peppertree invades a variety of habitats including old fields, forests, hammocks, ditches, and wetlands. It forms dense thickets that displace native vegetation. Brazilian peppertree is native to South America and was first introduced into the United States in the 1840s as an ornamental.
Selected Images
Maps
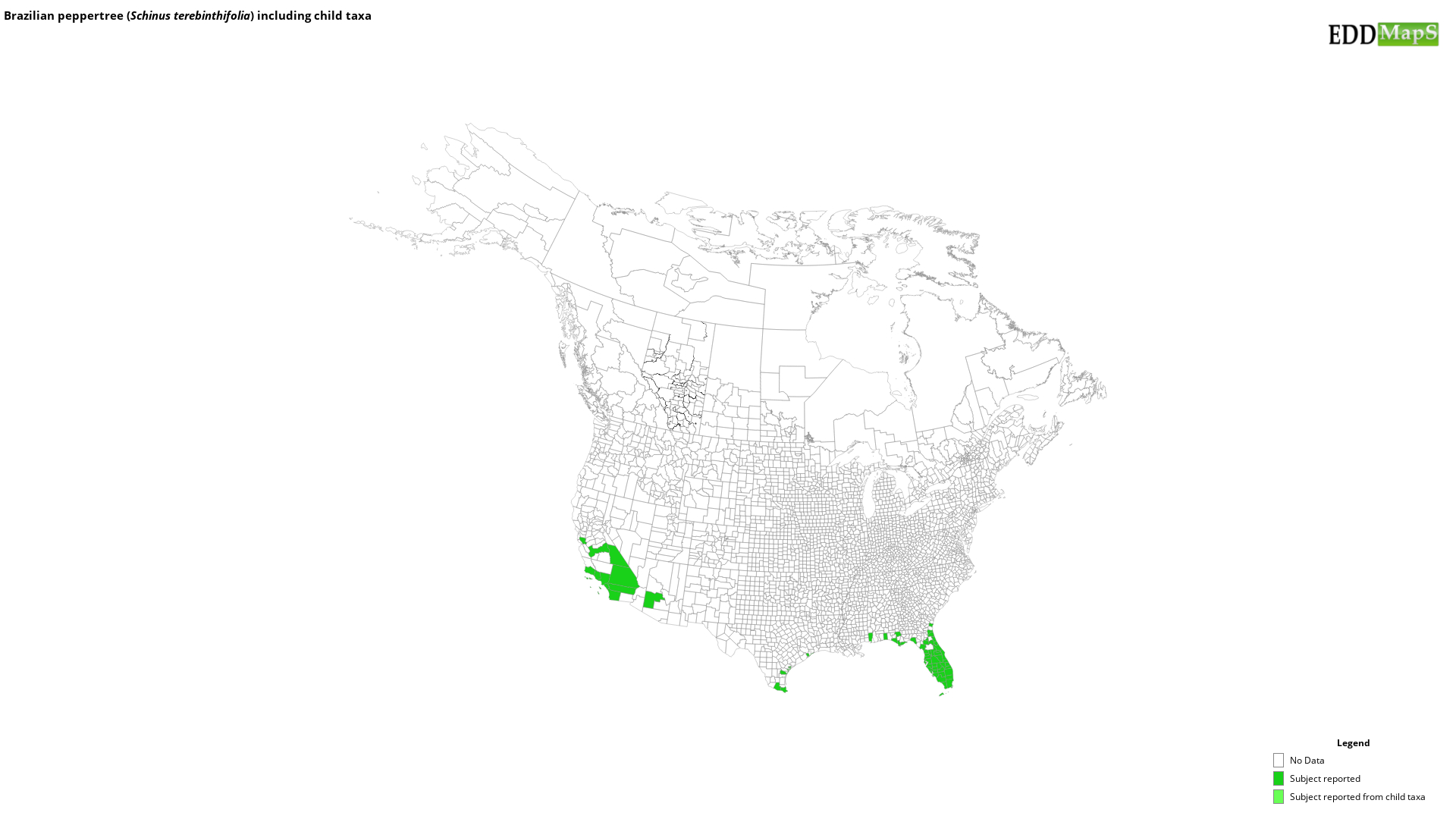
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
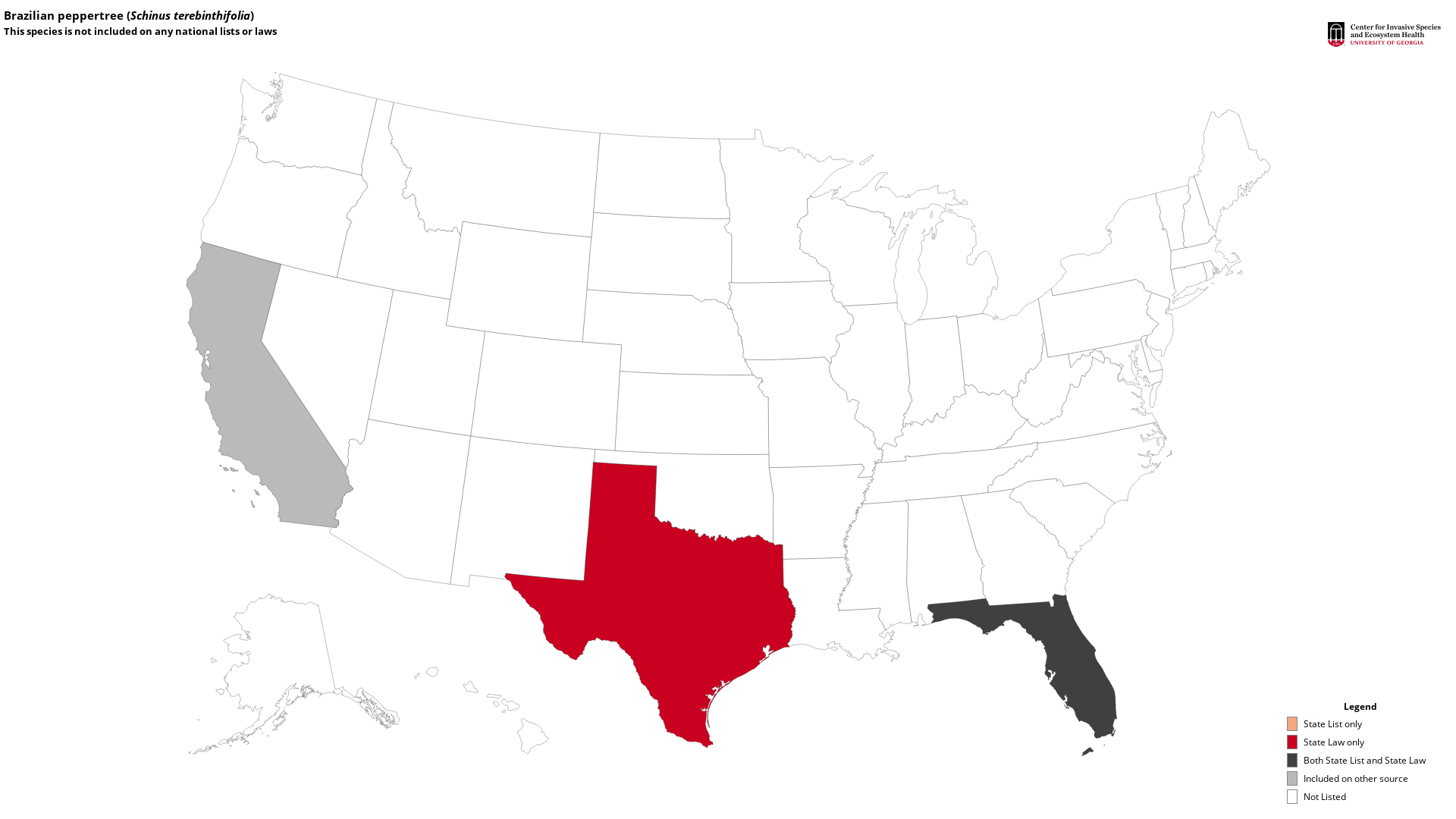
State List - This map identifies those states that list this species on their invasive species list or law. For more information, visit Invasive.org
Invasive Listing Sources
- California Invasive Plant Council
- Florida Invasive Plant Council - Plant List - Category I
- Florida Noxious Weeds
- Jil M. Swearingen, Survey of invasive plants occurring on National Park Service lands, 2000-2007
- John Randall, The Nature Conservancy, Survey of TNC Preserves, 1995.
- New Invaders of the Southeast
- New Invaders of the Southwest
- Nonnative Invasive Species in Southern Forest and Grassland Ecosystems
- Reichard, Sarah. 1994. Assessing the potential of invasiveness in woody plants introduced in North America. University of Washington Ph.D. dissertation.
- Southwest Florida Cooperative Invasive Species Mgmt. Area
- Texas Noxious Weeds
- WeedUS - Database of Plants Invading Natural Areas in the United States
Taxonomic Rank
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: Rosidae |
| Order: Sapindales |
| Family: Anacardiaceae |
| Genus: Schinus |
| Subject: Schinus terebinthifolia Raddi |
Synonyms and Other Names
Related Scientific Names:
Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi (Synonym)
References
Common Name Reference: Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) Online Database
Scientific Name Reference: Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) Online Database