common teasel
(Dipsacus fullonum)
Overview
- Appearance
- Dipsacus fullonum a biennial plant that exists as a basal rosette until flower stems develop.
- Foliage
- Rosette leaves are lanceolate to oblanceolate and stem leaves are opposite, lanceolate and fused at the base. All leaves have short prickles on the midvein.
- Flowers
- The erect flower stems reach 6 ft. (1.8 m) in height and support spiny flower heads that are covered with small, lavender to white flowers in April to September.
- Fruit
- Fruit is angled and approximately 0.08-0.12 in. (2-3 mm) long. Seeds are small and are dispersed by the wind after the seed-head has dried.
- Ecological Threat
- Dipsacus fullonum favors disturbed sites such as roadsides, ditches, waste places, riparian sites, fields and pastures in most of the continental United States. Only recently was Dipsacus fullonum distinguished from fullers teasel which was once cultivated for the dried flower heads used in wool processing. It is native to Europe.
Resources
- Weed Field Guide - USDA Forest Service
- Vegetation Management Guide - Illinois Nature Preserves Commission
Selected Images
Maps
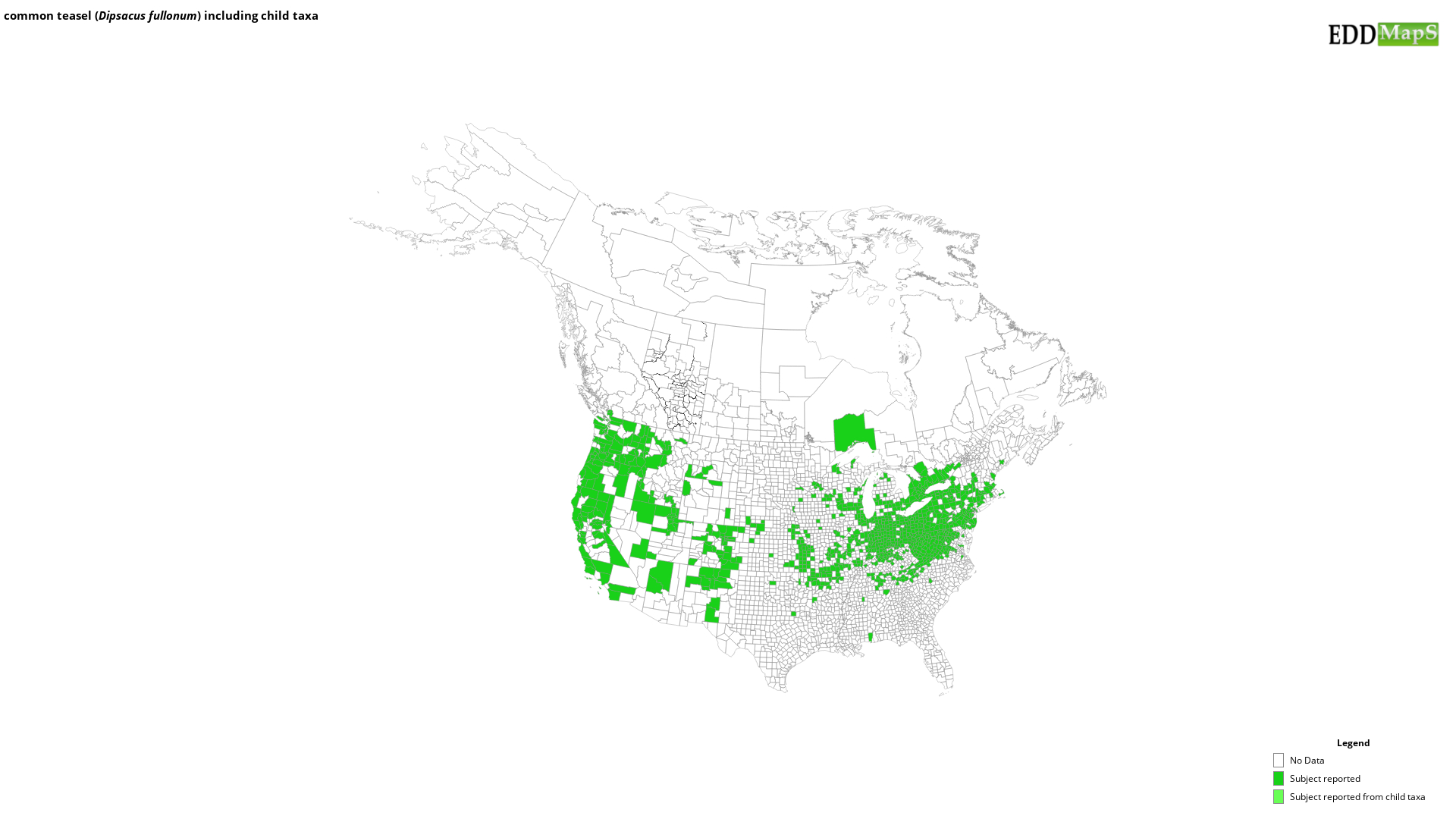
EDDMapS Distribution - This map is incomplete and is based only on current site and county level reports made by experts, herbaria, and literature. For more information, visit www.eddmaps.org
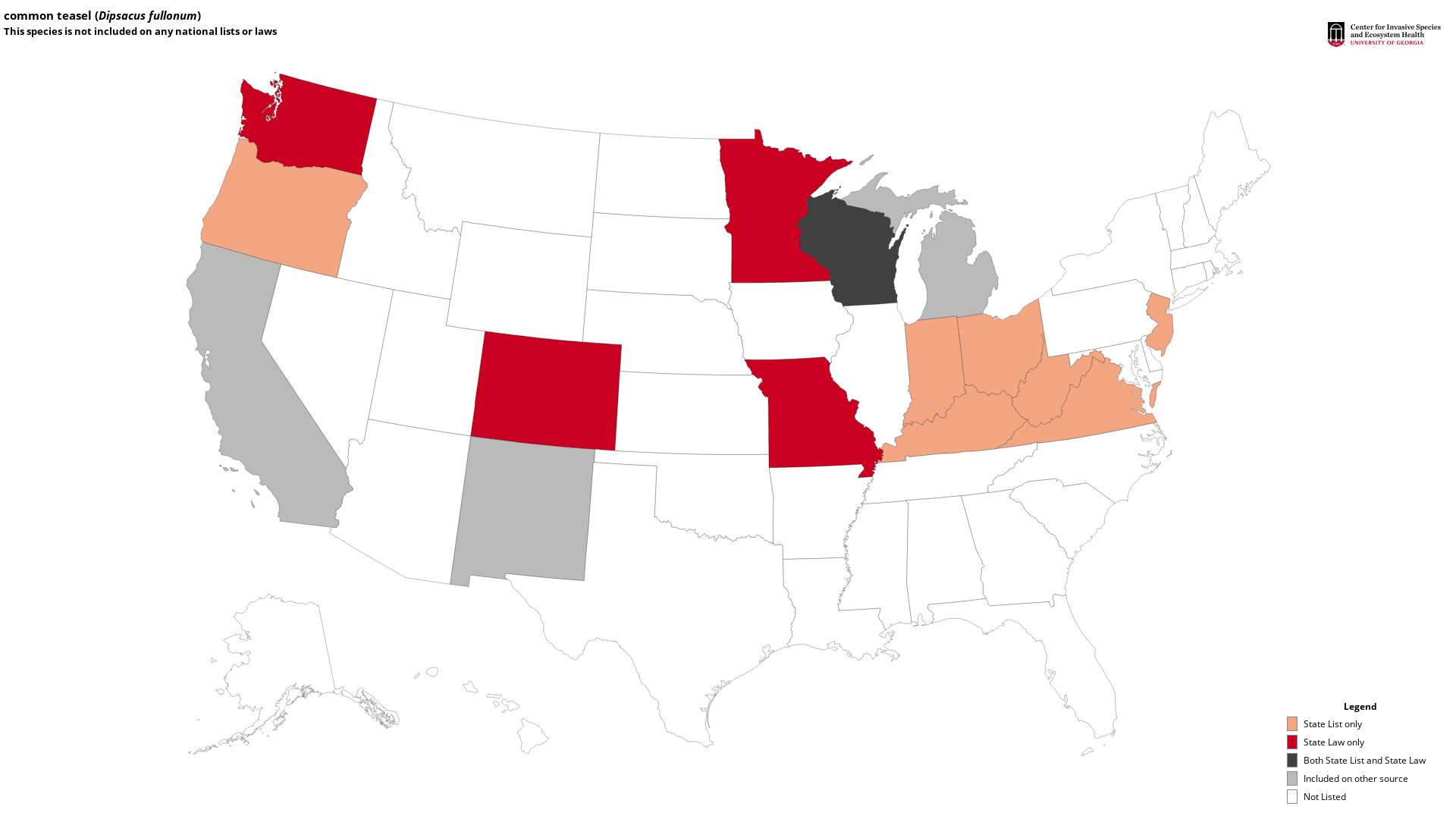
State List - This map identifies those states that list this species on their invasive species list or law. For more information, visit Invasive.org
Invasive Listing Sources
- California Invasive Plant Council
- City of Ann Arbor Michigan Parks and Recreation
- Colorado Noxious Weeds
- Hoffman, R. & K. Kearns, Eds. 1997. Wisconsin manual of control recommendations for ecologically invasive plants. Wisconsin Dept. Natural Resources, Bureau of Endangered Resources. Madison, Wisconsin. 102pp.
- Indiana Invasive Species Council - Invasive Plant List
- Indiana Terrestrial Plant Rule
- Invasive Plant Association of Wisconsin
- Invasive Plant Species of West Virginia
- Jil M. Swearingen, Survey of invasive plants occurring on National Park Service lands, 2000-2007
- John Randall, The Nature Conservancy, Survey of TNC Preserves, 1995.
- Kentucky Exotic Pest Plant Council - Significant Threat
- Minnesota Noxious Weeds
- Missouri Noxious Weeds
- Missouri SRISP Species List
- National Park Service, Mid-Atlantic Exotic Plant Management Team Invasive Plant List
- Native Plant Society of Oregon, 2008
- New Jersey Invasive Species Strike Team 2017 Invasive Species List
- New Mexico Noxious Weeds
- Nonnative Invasive Species in Southern Forest and Grassland Ecosystems
- Ohio Invasive Species Council
- Virginia Invasive Plant Species List
- Washington Noxious Weeds
- WeedUS - Database of Plants Invading Natural Areas in the United States
- West Virginia Invasive Species Strategic Plan and Volunteer Guidelines 2014
- West Virginia Native Plant Society, Flora West Virginia Project, and West Virginia Curatorial Database System, September 3, 1999
- Wisconsin Noxious Weeds
- Wisconsin's Invasive species rule – NR 40
Taxonomic Rank
| Kingdom: Plantae |
| Phylum: Magnoliophyta |
| Class: Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: Asteridae |
| Order: Dipsacales |
| Family: Dipsacaceae |
| Genus: Dipsacus |
| Subject: Dipsacus fullonum L. |
Other System Links
Plants: DIFU2
Bayer: DIWSI
GRIN: 14380
ITIS: 35404
NPDN Pest: PBOABBB
NPDN Host: 36355
Synonyms and Other Names
Other Common Names:
Fuller's teasel, teasel
Related Scientific Names:
Dipsacus fullonum ssp. sylvestris (Huds.) Clapham (Synonym)
Dipsacus sylvestris L. (Synonym)